Why Eutelsat Matters Now: The Birth of a Sovereign Giant
To begin, it is essential to understand one thing: Eutelsat is no longer the television satellite operator that many used to know. The company recently completed a radical transformation that now places it at the center of a global technological and geopolitical battle for control of internet from space.
The major turning point is the merger with OneWeb. By finalizing this deal, Eutelsat became the first company in the world to operate a fully integrated satellite fleet, combining traditional geostationary (GEO) satellites with a constellation of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites. In practical terms, this positions the group as the direct European competitor to American giants like SpaceX’s Starlink and Amazon’s Project Kuiper.
Furthermore, this transformation has a highly strategic dimension. In the context of the global tensions we are experiencing, controlling space-based communications has become a matter of digital sovereignty for Europe. Governments, particularly the French and British who are shareholders, see Eutelsat as a “strategic treasure.” In other words, the company is now a pillar of European autonomy, tasked with providing secure communications for governments, militaries, and critical infrastructure.
Finally, the financial and industrial stakes have been secured. The company’s ambitious €1.5 billion recapitalization plan, designed to fund the expansion of its OneWeb network, has now been fully secured. This was sealed this week after the United Kingdom confirmed a crucial investment of €163 million. This state-level support, alongside backing from major telecom players like Orange, underscores the strategic necessity of keeping Eutelsat competitive and ensuring Europe’s telecom resilience against the risks of cyberattacks or outages.
In conclusion, Eutelsat is in the spotlight today because the company has become Europe’s instrument of digital and industrial sovereignty in the race for satellite internet. It is a multi-billion euro battle with direct implications for our autonomy, our defense, and our technological future.
Sector Overview: A New Space Race in Satellite Communications
To understand Eutelsat’s strategic importance, we first need to look at the massive transformation happening in its industry. The satellite telecommunications sector is currently undergoing a revolution, driven by a fundamental shift in technology.
The Big Shift: From GEO to LEO Satellites
For decades, satellite communication relied on large, geostationary (GEO) satellites. Essentially, these are single, powerful satellites that orbit very far from Earth (about 36,000 km). While they can cover a wide area, their distance creates a significant time delay, or “latency,” making them unsuitable for real-time applications like video calls or online gaming.
Now, however, the industry is moving to Low Earth Orbit (LEO) constellations. This is a completely different approach. LEO constellations consist of thousands of smaller satellites that orbit much closer to Earth (around 500-2,000 km).
- The result? Much lower latency and higher bandwidth, making fast, responsive broadband internet possible anywhere on the planet.
- This shift is being fueled by a massive global demand for connectivity—for remote communities, for the Internet of Things (IoT), and for 5G mobile networks.
The Key Players and Government Interest
This new LEO market has sparked a new space race, with a few key players dominating the field:
| Company | Focus/Strengths |
| SpaceX/Starlink | Largest LEO constellation, global broadband, rapid deployment |
| Amazon Kuiper | Planned large LEO network, strong financial backing |
| SES | Hybrid GEO/LEO/MEO fleet, enterprise and government services |
| Telesat | LEO constellation (Lightspeed), focus on enterprise and government |
- SpaceX (Starlink): The current leader, with the largest and most advanced LEO constellation.
- Amazon (Project Kuiper): A major future competitor with huge financial backing.
- Eutelsat Group (with OneWeb): Positioned as the European champion in this global race.
Furthermore, this isn’t just a commercial competition; governments are deeply invested. Control over satellite networks is now seen as essential for national security and strategic autonomy. For instance, these networks are critical for:
- Secure military and government communications.
- Providing internet to rural and remote areas.
- Ensuring infrastructure resilience in case of natural disasters or cyberattacks.
Market Outlook and Key Challenges
The future for this sector is bright. The global satellite internet market is expected to grow dramatically, exceeding $100 billion by 2030.
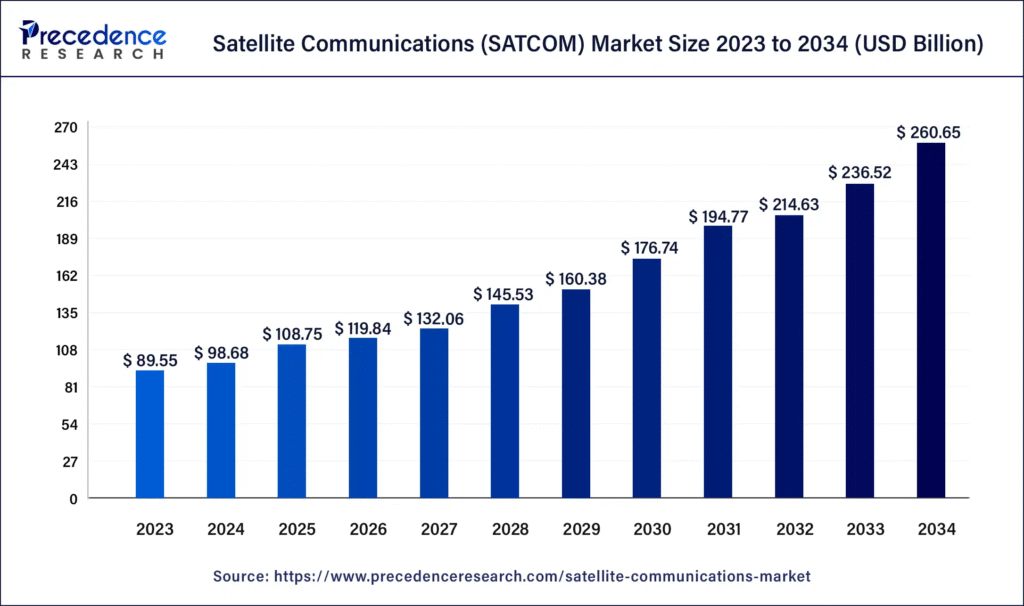
- LEO revolution: Rapid deployment of LEO satellites, smallsats, and cubesats is driving new applications and expanding the market.
- Technological innovation: Advances in flat-panel antennas, AI-driven network management, and optical communications are enhancing performance and enabling new services.
- North American leadership: The US leads in satellite internet deployment and infrastructure, but Europe and Asia are ramping up investment and policy suppor
However, the industry also faces significant challenges. These include the high cost of deploying and maintaining thousands of satellites (capital intensity), the risk of creating too much traffic in space, and the need to navigate complex international regulations.
In conclusion, the shift to LEO constellations is redefining the entire satellite industry. It has intensified competition and raised the stakes for governments seeking secure and independent communications, placing companies like Eutelsat at the center of a strategic and fast-growing global market.
Focus on the Company: Eutelsat’s Strategic Transformation
Now that we understand the satellite industry’s massive shift, let’s focus on how Eutelsat fits into this new world. The company has undergone one of the most significant transformations in its history to become a central player in the race for global connectivity.
From Legacy TV to Modern Connectivity
For decades, Eutelsat was primarily known for its geostationary (GEO) satellites. In simple terms, its main business was broadcasting television signals across Europe, the Middle East, and Africa. This was a stable and profitable business, but it faced slowing growth as the world moved towards internet-based streaming.
Recognizing this shift, Eutelsat made a bold and transformative move.
The Game-Changer: The Merger with OneWeb
In September 2023, Eutelsat completed its merger with OneWeb, a company with a massive constellation of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites. This deal created the world’s first fully integrated satellite operator with both GEO and LEO fleets, now known as Eutelsat Group.
So, what does this mean? It means the company can now offer the best of both worlds:
- GEO satellites for wide coverage applications like television broadcasting.
- LEO satellites for high-speed, low-latency internet connectivity, targeting markets like mobile network backhaul, corporate networks, governments, and in-flight connectivity.
This unique hybrid model allows Eutelsat to provide flexible and resilient solutions that purely LEO competitors, like Starlink, cannot match.
A Look at the Financials: Investing for Growth
This massive transformation has had a major impact on the company’s financials, showing a clear story of short-term pain for long-term gain.
- Revenue and EBITDA: In its first year after the merger, the group reported strong revenues from its core businesses of €1.27 billion and an adjusted EBITDA of €698 million. This shows the underlying business remains solid.
- The Cost of a New Fleet (CapEx & Debt): However, the huge investment (CapEx, or capital expenditures) required to build and launch the OneWeb LEO constellation is very high. As a result, the company reported a net loss of €310 million for the year, a major swing from a net profit the year before. The company’s debt levels are also high, which is typical for large infrastructure projects like this.
- The Future Outlook: Despite the current loss, management is confident in the future. They project double-digit revenue and EBITDA growth in the coming years, aiming for revenues of €2 billion by 2027 as the new LEO services ramp up and start generating significant income.
Competitive Positioning: Eutelsat vs. Starlink
In this new market, Eutelsat’s main competitor is clearly SpaceX’s Starlink.
| Aspect | Eutelsat | SpaceX / Starlink |
| Satellite Orbits | GEO + LEO (hybrid) | LEO only |
| Core Markets | Broadcast, enterprise, government, B2B | Consumer broadband, B2B |
| Geographic Focus | Europe, Africa, global | Global |
| Ownership/Backing | French & UK governments, European funds | Private (SpaceX) |
| Financial Outlook | Double-digit growth targeted, recent net loss | Rapid revenue growth, private financials |
However, they are not fighting on the exact same battlefield. While Starlink has focused on and is dominating the direct-to-consumer internet market, Eutelsat is leveraging its long-standing relationships and hybrid network to target a different set of customers:
- Governments and Defense agencies, who require secure and sovereign communications.
- Large Corporations and Telecom companies, who need reliable connectivity for their networks.
- Aviation and Maritime industries, for in-flight and on-ship internet.
In conclusion, Eutelsat has transformed itself from a legacy media company into a vital global connectivity player. While this strategic pivot has been expensive and has impacted its short-term profitability, it has positioned the company to compete in the fastest-growing segment of the satellite market for decades to come.
Valuation and Market Perception
Now that we understand the company’s new strategy, we need to look at its financials and how investors currently perceive the stock. The picture is one of a company that appears cheap on some metrics, but is weighed down by the heavy costs of its transformation.
A Snapshot of the Numbers
Here are the key valuation metrics for Eutelsat Group:
| Metric | Value |
| Stock Price | €3.6 |
| Market Cap | €1.63B |
| Entreprise Value | €4.4B |
| EBITDA | €718.9M |
| EV/EBITDA | 5.89 |
| Net Income | €-873M |
| Free Cash Flow | €837M |
| ROE | -28.26% |
| Government Support | High |
- Stock Price: trading around €3.60
- Market Capitalization: €1.63 billion
- Enterprise Value (EV): €4.4 billion. (This higher number includes the company’s significant debt).
- EV/EBITDA Ratio: 5.89x. This key multiple is relatively low, suggesting the company is not expensive compared to its operating earnings.
- Net Income & ROE: The company has a net loss of -€873 million and a negative Return on Equity (ROE) of -28.26%. This is a direct result of the high costs and accounting charges related to the OneWeb merger.
How the Market Views Eutelsat
These numbers lead to a very mixed and cautious perception of the company on Wall Street.
On the one hand, there is a strong “value” argument. The stock appears cheap based on its assets and its EV/EBITDA multiple. Furthermore, the company has powerful government backing. The French and UK governments are major shareholders and consider the company a “strategic asset” for Europe’s digital sovereignty. This provides a strong level of support.
On the other hand, the market is worried.
- The high debt used to finance the LEO constellation is a major concern for investors.
- The current net loss shows that the company is in a difficult transition period.
- No dividend: The company is not currently paying a dividend, as it is reinvesting all its cash into building out the OneWeb network.
In conclusion, Eutelsat is currently a classic “battleground stock.” Value investors and those focused on long-term strategy see a deeply undervalued, strategic European champion. However, more cautious investors see a company with high debt, no current profits, and significant execution risk. This division explains why the stock price is so low despite the company’s strategic importance.
Of course. Based on this excellent and detailed summary, I have created the final analytical section of the newsletter.
This section lays out the bull case (the opportunities) and the bear case (the risks) to give readers a complete and balanced picture before the final recommendation.
The Investment Thesis: Opportunities vs. Risks
Eutelsat today stands at a major turning point. The company has unique opportunities ahead, but it also faces significant challenges. A smart investment decision requires looking at both sides of the coin.
The Opportunities (The Bull Case)
First and foremost, Eutelsat is positioned in a massively growing market. The global market for LEO satellite internet is expected to grow by over 18% per year, surging from about $7 billion today to over $26 billion by 2033. Eutelsat is one of the only companies in the world with a fully operational network ready to capture this demand, especially in fast-growing business-to-business (B2B) connectivity.
Furthermore, it has a unique strategic position. In a world dominated by American (Starlink, Kuiper) and Chinese satellite ambitions, Eutelsat is the leading non-US/China LEO operator. This makes it the default choice for governments and global companies seeking a secure and independent alternative for their satellite communication needs.
In addition, the company is building powerful partnerships. Eutelsat is not going it alone. It has already secured multi-year deals with major telecom giants like Orange to provide LEO services to their enterprise customers. It is also a key partner in the European Union’s own secure satellite program, which solidifies its role as a strategic asset for Europe.
The Risks to Watch (The Bear Case)
However, the path forward is not without major challenges.
The biggest risk is the immense cost of this business. Building and maintaining a satellite constellation requires a huge amount of capital (CapEx). Eutelsat is raising over €1.3 billion just for the next phase of its network. Moreover, the return on this investment is not guaranteed, and the company will need to continuously invest to replace older satellites and keep its technology up to date.
Next, the competition is intense. Starlink already has over 7,500 satellites in orbit compared to Eutelsat’s ~650, giving it far greater capacity. At the same time, Amazon’s Project Kuiper is also entering the race with huge financial backing. Eutelsat must invest heavily in its next-generation satellites just to keep pace.
Finally, there are technical and financial risks. Launching and operating thousands of satellites is incredibly complex, and there are always risks of delays or launch failures. On top of this, since Eutelsat earns revenue in euros but often buys its satellites and launches in US dollars, a strengthening dollar can hurt its profit margins.
Conclusion: Is Eutelsat a Good Investment?
After our deep dive into Eutelsat’s massive transformation, the booming satellite sector, and the significant risks and opportunities, we can answer the final question: Should you invest in Eutelsat today?
The company presents a fascinating and complex case. It’s a “battleground” stock with strong arguments on both sides.
- The Bull Case (The Opportunity): Investors are looking at a company that is now a strategic European champion in the critical satellite internet market. It has powerful government backing, a unique hybrid (LEO/GEO) network that competitors lack, and is positioned in a market set for explosive growth. On some metrics, like its EV/EBITDA ratio of 5.89x, the stock appears very cheap for such a strategic asset.
- The Bear Case (The Risk): However, the company is facing immense challenges. It has high debt, is currently not profitable due to the massive investments in its OneWeb constellation, and faces brutal competition from larger, faster-moving rivals like Starlink. The execution risk is very high.
Final Recommendation: A Speculative Buy for Patient, Long-Term Investors
So, is Eutelsat a value play or a speculative growth bet? The answer is that it’s a unique mix of both. It has the low valuation of a value stock but the high-risk, high-potential profile of a speculative growth company.
Therefore, our final recommendation is a Speculative Buy, but only for investors with a long-term time horizon (3-5+ years) and a high tolerance for risk.
This is not a stock for short-term traders or those seeking immediate profits. Instead, it is a bet on the long-term strategic value of Europe having its own sovereign, global satellite internet constellation. The powerful backing of the French and UK governments provides a significant safety net.
Call to Action for Investors: For those interested in this story, the key things to track are:
- New Government & Enterprise Contracts: Watch for announcements of major deals for its LEO services.
- Progress on Profitability: Keep an eye on the company’s financial reports to see if they are on track to return to profitability as their LEO revenue grows.
- Future CapEx Plans: Monitor announcements about the cost and timeline for their next-generation satellite constellation.

