Strait of Hormuz Blockade: A New Flashpoint Threatening Global Energy SecuritY AND OIL & PETROLEUM
Strait of Hormuz, global energy supply, Middle East tensions, Iran blockade, oil transport chokepoint, US-Israel conflict, Asian energy security
A Strategic Strait at the Brink OF CONFLICT
In a rapidly escalating geopolitical landscape, the Strait of Hormuz — the world’s most critical oil chokepoint — has once again come under the spotlight.
As reported by CNBC, BBC , rising tensions involving the US, Israel, Iran, and increasingly China have brought fears of a blockade or full closure of this narrow waterway — a scenario with catastrophic implications for global energy markets.
Why the Strait of Hormuz Matters So Much
Located between Oman and Iran, the Strait of Hormuz is just 21 miles wide at its narrowest point, yet it handles nearly 20% of the world’s daily oil consumption — that’s over 17 million barrels per day.
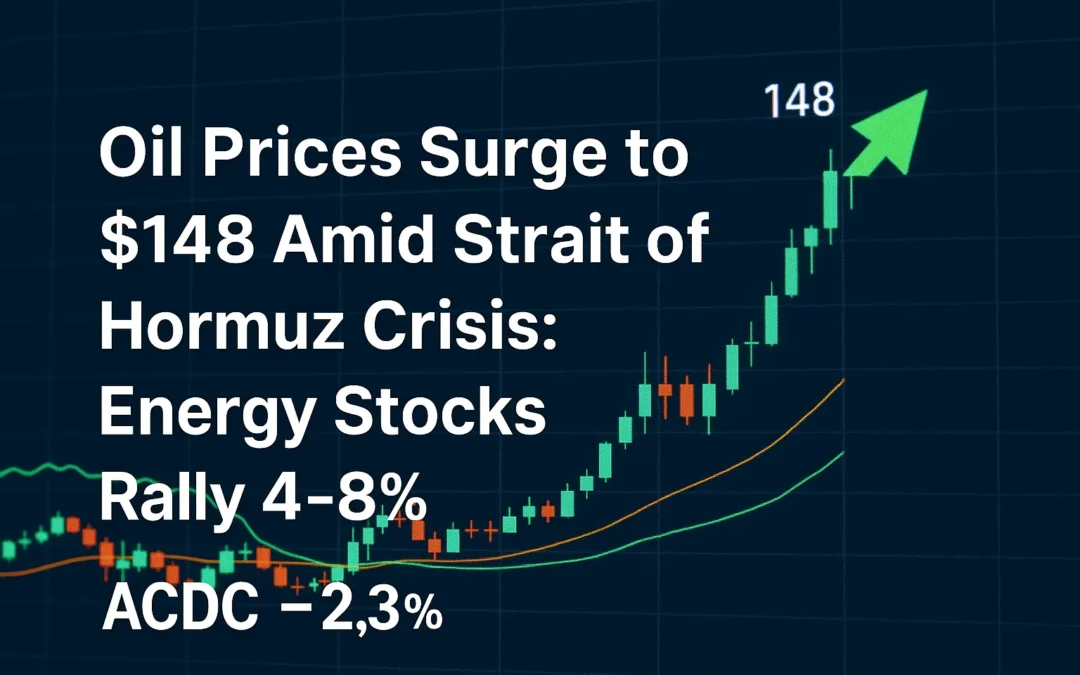
The potential blockade of the Strait of Hormuz could lead to significant increases in oil prices, estimated to rise by $8.25 to $31.25 per barrel.
If oil prices exceed $90 per barrel, ACDC’s operational costs may rise by approximately 15%, potentially reducing profit margins and leading to a projected 10-15% decline in stock value due to decreased consumer spending and market volatility . Increased geopolitical risks may lead to heightened market volatility, impacting investor confidence.
ACDC’s stock performance could be negatively influenced by market reactions to energy supply uncertainties.
It is not just vital for oil. The strait is also a critical artery for liquefied natural gas (LNG), especially from Qatar, the world’s second-largest LNG exporter. Any disruption to its flow immediately sends shockwaves through Asian economies, especially India, China, Japan, and South Korea, all of which are highly dependent on Gulf energy imports.
The Current Crisis: What’s at Stake?
According to recent U.S. military and intelligence reports, Iran is signaling intentions to restrict passage through the strait, possibly in retaliation to Israeli airstrikes and U.S. sanctions. With Chinese naval vessels also reported near the Arabian Sea, the Strait is becoming a hotbed of military posturing.
If the blockade becomes reality:
- Global oil prices could spike beyond $150/barrel, triggering inflation.
- Asian economies could face severe energy shortages and increased import bills.
- Global shipping and trade routes would need expensive re-routing.
- Strategic reserves would come under pressure, potentially triggering emergency energy alliances.
Asia’s Energy Dependency: No Easy Alternatives
Asia accounts for over 70% of the oil and gas shipped through the Strait of Hormuz. Countries like India and China have tried to diversify via pipelines and renewable investments, but the region remains dangerously reliant on Gulf oil.
Key implications for Asia:
- China’s Belt and Road Initiative faces disruption in key energy corridors .
- India’s import bill could surge, worsening its trade deficit.
- Japan and South Korea, with limited domestic energy production, may be forced to outbid rivals for LNG.
Global Energy Markets and Strategic Calculations
Beyond Asia, Europe and North America would not be immune. While the U.S. has increased domestic production, its allies in Europe would see energy insecurity ripple through industrial and consumer sectors.
In response, the world may see:
- Accelerated renewable energy investment
- Strategic reserves being tapped simultaneously
- Re-evaluation of maritime security doctrines
Conclusion: Strait of Hormuz—A Small Strait with Global Consequences
The situation unfolding in the Strait of Hormuz is more than a regional crisis — it’s a litmus test for global energy security in a multipolar world. With nations watching nervously, any blockade could represent the most serious disruption to global oil flow since the 1973 oil embargo.
For Asia and the world, ensuring uninterrupted access through the Strait is not just a matter of trade — it’s a matter of economic stability and strategic survival.